KPI stands for Key Performance Indicator. This is the era of competition and we have to survive with a global challenge in the apparel industry. If you carefully work with Key points that are KPI Factors of Garments then surely Garments business will flourish. The management team should focus on KPI for their industry. KPI report will help you to look into the actual condition of your garments.
KPI Factors of Garments
There are many KPI factors that are directly and indirectly related to garments, especially in factory operations.
KPI for Garments Cutting
Cutting Efficiency
Cutting efficiency one of the most important factors. If an efficiency increase in the cutting section then production will increase by using a minimum number of workforce.
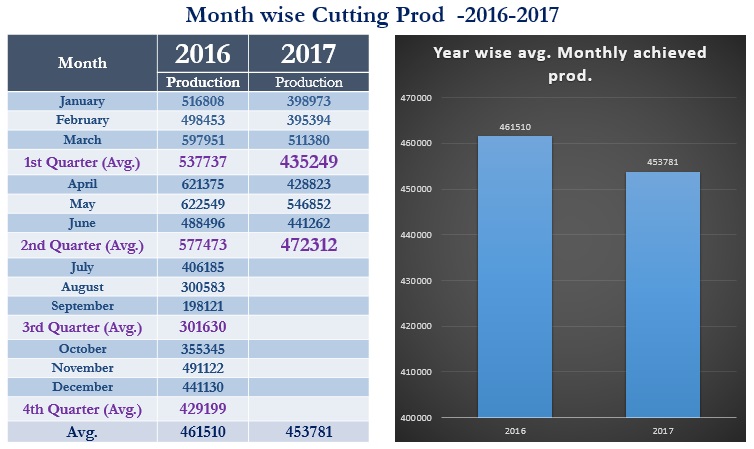
 Cutting Production
Cutting Production
Cutting production is another important factor as like Cutting efficiency. Cutting production is related to Spreading, cutting, numbering, and bundling.
DHU (Defect per Hundred Units) in Cutting
In cutting, there is no way to repair the defect, must replace panel as per marker with shade matching. So if DHU is high, you will be needed to rework.
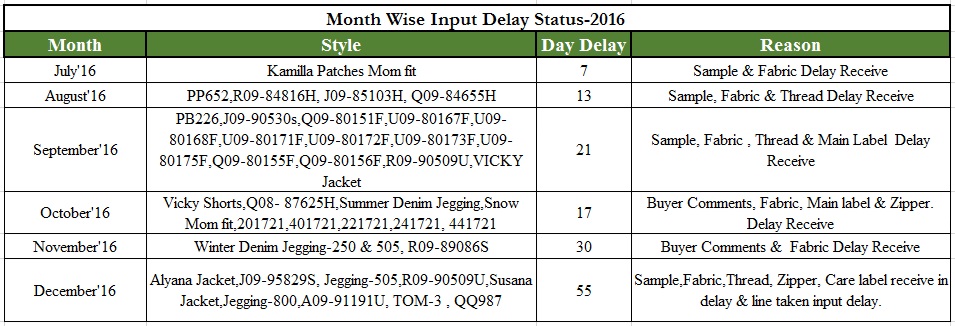
Cutting Delay/Input Delay in Sewing Line
Sometimes cutting and sewing does not start as per plan. Only two reasons behind this. If PP/Size Set or pilot run samples fail to buyer QC to meet the quality standard, apparel manufacturers have remake samples and submit again to buyer QC to pass samples and get cutting approval. Sewing can be delayed for Trims and accessories delay receive from the supplier.
KPI for Sewing
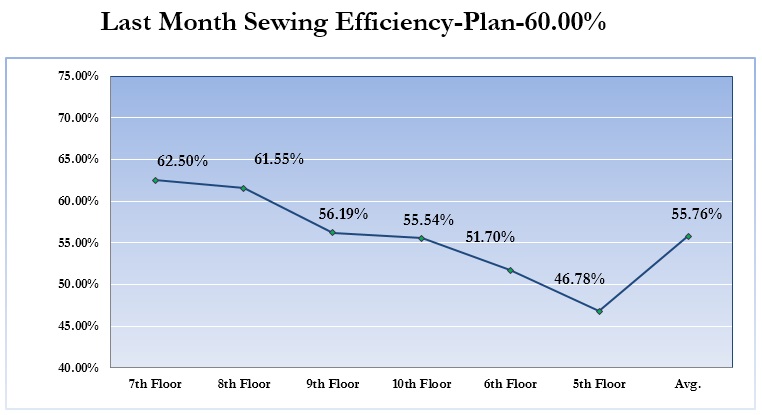
Line Wise Sewing Efficiency
Sewing makes the whole garments, so sewing efficiency is an important factor for the garments industry.
Efficiency Calculation
An operator was doing an operation of SAM (Standard Allowed Minute) 0.60 minutes. In 10 hours of the day, he produces 600 pieces. So according to the efficiency calculating formula, that operator’s overall efficiency is as follows:
Efficiency (%) = [Total minute produced by an operator/Total minute attended by him *100]
Efficiency (%) = [(Total piece made X SAM of the operation)/ (Total working hour X 60) * 100]
= [(400 x 0.60) / (10 X 60)*100%]
= 240/600*100%
= 40.00%
Production/Hour/Manpower/Machine
The ratio among production/hour/manpower/machine is to be optimal. Every factory has self-study to reduce manpower, keeping less helper with the best possible production outcome.
Machine Trouble/Machine Downtime
Because of Machine trouble production is stopped. The machine maintenance department has to do their best effort to reduce machine downtime. An electrical problem also can be the cause of Machine trouble/machine downtime.
DHU in Sewing
Defects rate also a key point in garments manufacturing. The factory has to rework for repairing defects. The defect generation reduces the operator’s efficiency. The factory wants to keep defects as low as possible for per hundred units.
Absenteeism
Operator absenteeism hampers sewing production, creates the bottleneck. Every factory target employee absenteeism rate is zero % but sometimes it may not possible to keep this percent.
No. Style Change
Style change effect on productivity, efficiency, and quality. So the garments manufacturer wants big lot order more rather than small quantity order for any lot.
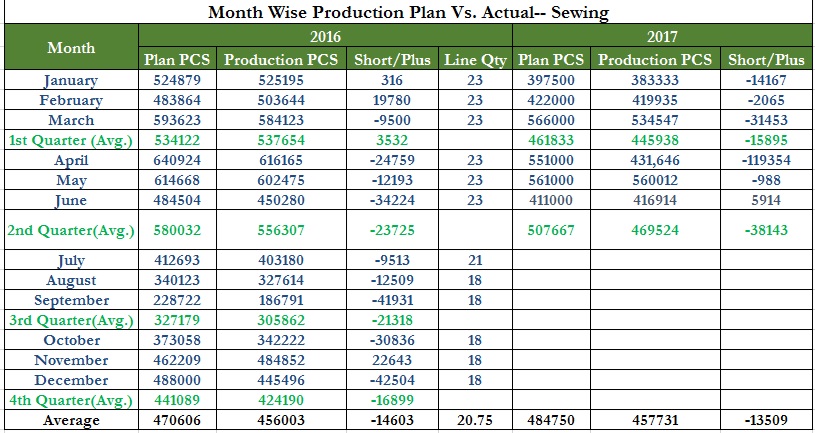
Plan vs Actual Production Ratio
All factories have the planning department to make a plan for cutting, sewing, finishing, and shipment to meet buyer required shipment date. The gap between plan and actual production is the reason for not meeting on-time delivery.
Idle Time/Machine
Idle time is also known as loss of time. For any type of reason, operators are not working and are considered to lose time. Common reasons for idle time are; using a new layout, machine trouble, no work, etc.
Operator Wise Efficiency
The best way of efficiency calculation is to calculate individual operator efficiency every day, show report weekly, and train up lower efficient operator for improvement which ultimately increases the operational efficiency.
Process Improvement
Industrial engineering (IE) department do time study, motion study, and work-study to find out SMV (Standard Minute Value), to minimize unnecessary motion for sewing operations. In this way, the factory saves SMV time for garments manufacturing.
Operator Turnover Rate
Since sewing is the key process of apparel, sewing operator turnover percentage is important. Turnover means the number of employees got fired or left from the job and replaced at the workplace by a new operator. If the turnover rate is lower in the factory then it will be better for the company.
Monthly turnover % = (Employees separated/Average number of employees during the month) *100
Example, If Employees separated = 21, Average number of employees during the month= 950
So, Monthly Turnover % = (21/950) × 100 = 2.21%
KPI for Trims and Fabrics
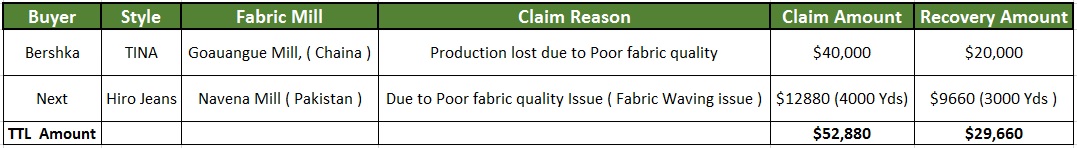
Claim Amount vs. Recovery Amount
According to the buyer quality standard, garments manufacture has to reject fabrics, trim if there is any quality issue. So, the maker must claim for compensation by replacing or giving back their money.
KPI for Finishing, Final Audit, and Shipment
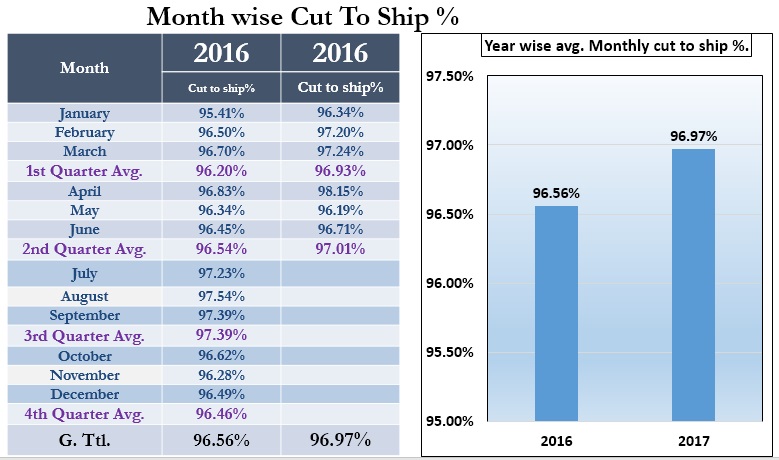
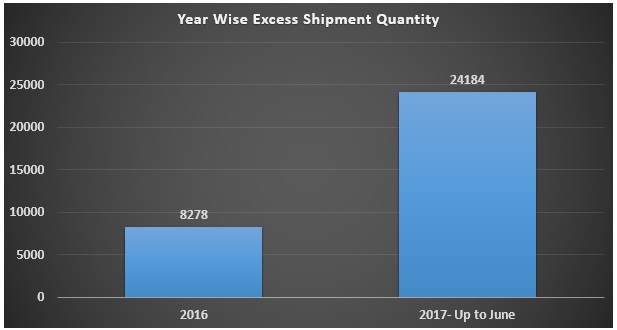
Cut to Ship Quantity
As PO wise buyer order quantity cutting department try to cut extra as much as possible. It could be from 2% to 5%. GMTS reject due to a different quality issue. Below data will give an idea about GMTS (Garments) production flow.
Reject Percentage
For some critical quality problems like wash damage, measurement out of tolerance, work hole, and unrepeatable problems GMTS rejected by finishing the quality team.
DHU in Finishing
Defects rate also a key point in garments manufacturing. The factory has to rework to repair defects. The finishing team has to repair whatever defect comes from sewing or finishing they found. The factory wants to keep defects per hundred units as low as possible. If too many products are defected then to rework the garments may add extra cost to the product which to totally unexpected.
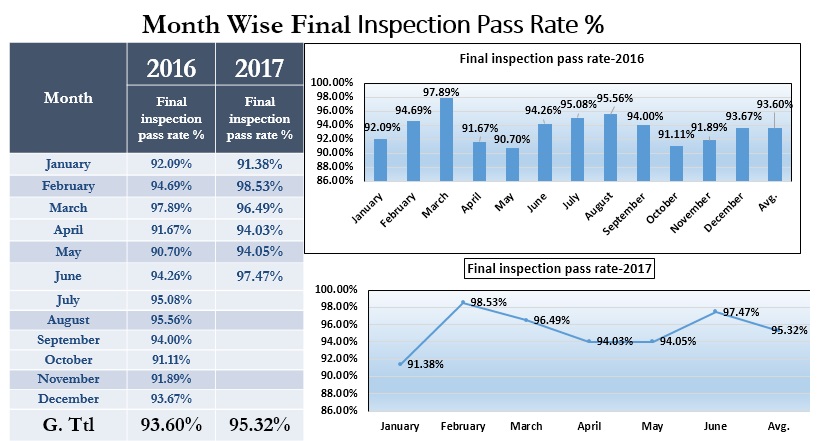
Final Audit Pass Rate
The final Audit pass rate is the number 1 KPI factor for Garments Quality. For some buyer final audit, if fail once any PO in final Audit, Factory has to give a penalty for that. Any PO fail in the final audit, a factory has rechecked the full quantity of goods again. Could imagine how much cost need to recheck, and it also does hamper running production as well.
Finishing Production
Finishing is the last step in apparel manufacturing. On-time delivery, sea, or air shipment mainly depends on the finishing of production.
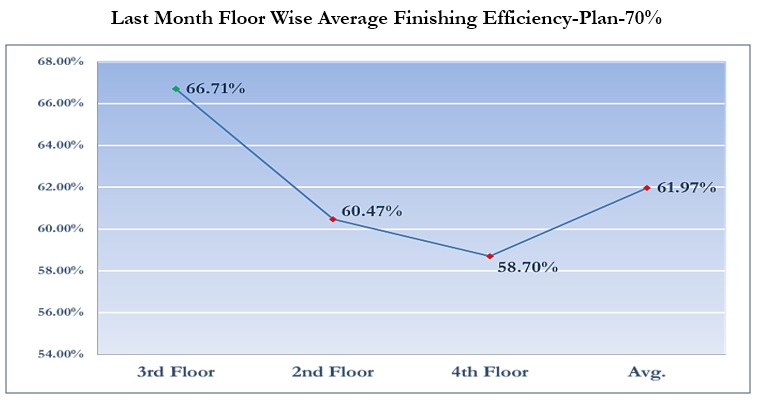
Finishing Efficiency
Finishing efficiency is also a very important key factory. If efficiency increases, production will increase with minimum manpower, and ultimately it will increase profit for the company.
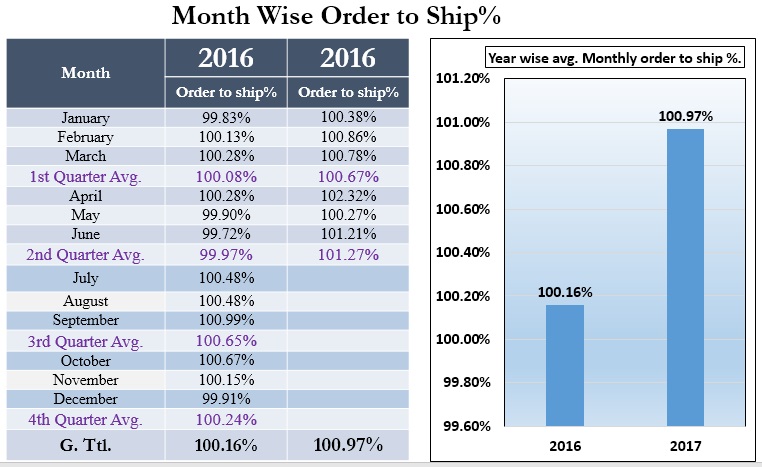
Order and Ship Ratio
Order and ship ratio should be equal at least or ship quantity could be more than order quantity since cutting quantity is more than 2% or 3% of the order quantity by reducing reject %.
AirShip Quantity
Two reasons are the cause for air shipment. One, If Garments maker cannot meet on-time delivery date then the maker has to ship goods by air at his own cost. GMTS suffer a huge financial loss for air shipment because the rate is more for air shipment. Number two would be merchandising reasons for not sourcing raw material on time.
Templates and KPI Dashboard Presentation
You may need to present your factory KPI data with Top management or may need to report them. Here I am sharing you a complete presentation and Excel database for your convenience for free. I hope these would help you to work with KPI smoothly.
- KPI Presentation-Apparel and Garments (PowerPoint) (1mb)
- Summary of KPI report (Excel) (1.3mb)






I got your thought nice one.
it is my interest to keep it!!! , and go beyond your current performance.
yours
haftu hiluf from Tigray region, Ethiopia
Thank you so much for sharing.