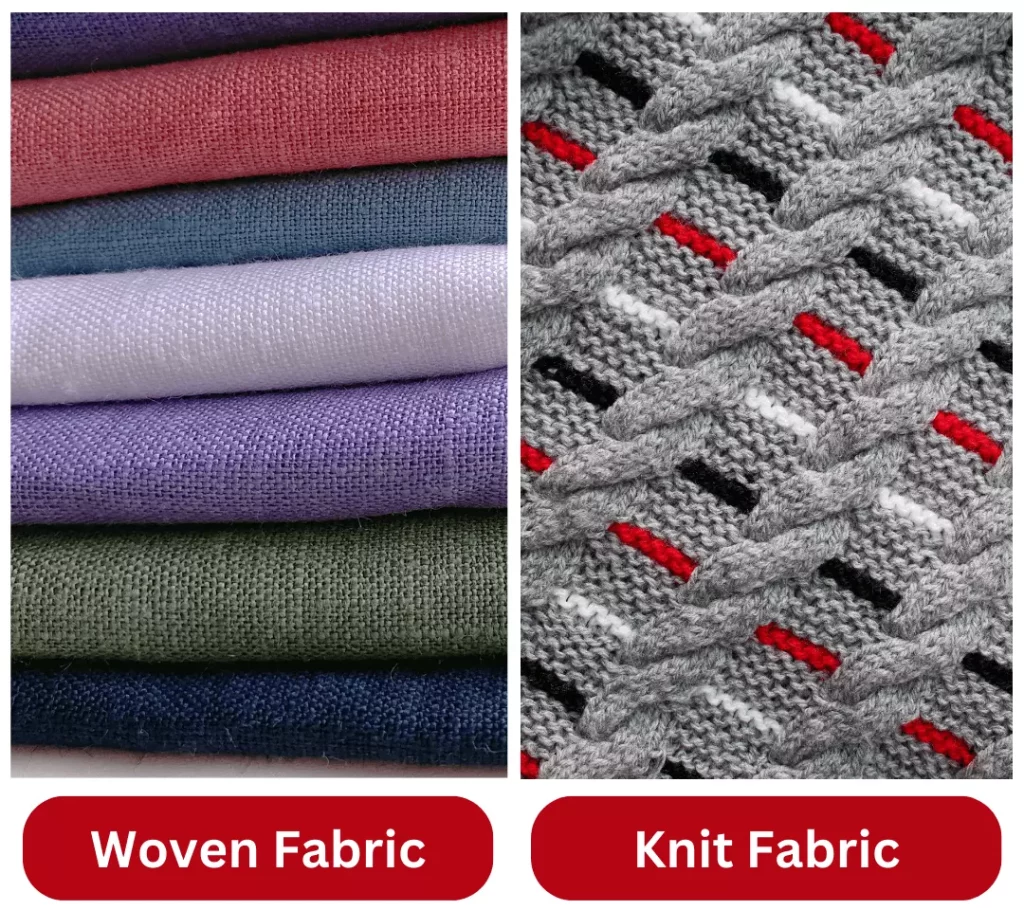
Woven and knit fabrics are two distinct types of fabrics used in the apparel industry. Woven fabrics are made by interlacing two sets of yarns at right angles to each other, creating a flat, stable fabric. In contrast, knit fabrics are made by interlocking loops of yarn, creating a stretchy, flexible fabric. In this article, we will share the difference between woven and knitted fabric. Let’s look at each type in more detail:

Woven Fabric
Woven fabrics are created on a loom by interlacing yarns at right angles to each other. This fabric is generally more stable and less stretchy than knit fabrics, which makes them ideal for garments that require structure, such as dress shirts, suits, and trousers. It can be made from a variety of fibers, including cotton, linen, wool, silk, and synthetic materials like polyester and nylon.
One of the most significant benefits of woven fabrics is that they can be tailored easily. They can be cut and sewn into a range of shapes and sizes without distorting the fabric’s structure. This allows for intricate patterns and designs to be created on woven garments. Additionally, woven fabrics are generally more durable than knit fabrics, making them a popular choice for workwear and uniforms.
Knit Fabric
Knit fabrics are made by interlocking loops of yarn, creating a stretchy and flexible fabric. It can be made in a variety of ways, including by hand, on a knitting machine, or by using circular knitting methods. Knit fabrics can be made from a range of fibers, including wool, cotton, silk, and synthetic materials like polyester and nylon.
One of the most significant benefits of knit fabrics is their stretch and flexibility. This makes them ideal for garments that require comfort and ease of movement, such as athletic wear, leggings, and t-shirts. Knit fabrics are also typically lighter and more breathable than woven fabrics, making them ideal for warm weather clothing.
Knit fabrics are generally less durable than woven fabrics, and they can be more challenging to tailor due to their stretch and flexibility. However, advances in technology have allowed for more robust and durable knit fabrics to be created, making them a more versatile choice for a range of garments.
23 Difference between Woven and Knitted Fabric
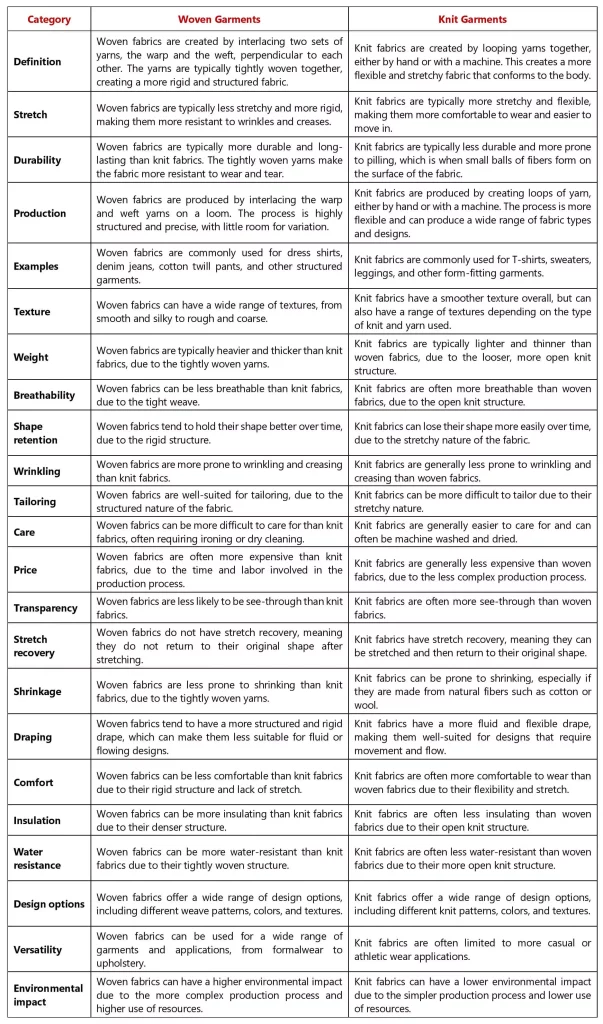
| Category | Woven Garments | Knit Garments |
| Definition | Woven fabrics are created by interlacing two sets of yarns, the warp and the weft, perpendicular to each other. The yarns are typically tightly woven together, creating a more rigid and structured fabric. | Knit fabrics are created by looping yarns together, either by hand or with a machine. This creates a more flexible and stretchy fabric that conforms to the body. |
| Stretch | Woven fabrics are typically less stretchy and more rigid, making them more resistant to wrinkles and creases. | Knit fabrics are typically more stretchy and flexible, making them more comfortable to wear and easier to move in. |
| Durability | Woven fabrics are typically more durable and long-lasting than knit fabrics. The tightly woven yarns make the fabric more resistant to wear and tear. | Knit fabrics are typically less durable and more prone to pilling, which is when small balls of fibers form on the surface of the fabric. |
| Production | Woven fabrics are produced by interlacing the warp and weft yarns on a loom. The process is highly structured and precise, with little room for variation. | Knit fabrics are produced by creating loops of yarn, either by hand or with a machine. The process is more flexible and can produce a wide range of fabric types and designs. |
| Examples | Woven fabrics are commonly used for dress shirts, denim jeans, cotton twill pants, and other structured garments. | Knit fabrics are commonly used for T-shirts, sweaters, leggings, and other form-fitting garments. |
| Texture | Woven fabrics can have a wide range of textures, from smooth and silky to rough and coarse. | Knit fabrics have a smoother texture overall, but can also have a range of textures depending on the type of knit and yarn used. |
| Weight | Woven fabrics are typically heavier and thicker than knit fabrics, due to the tightly woven yarns. | Knit fabrics are typically lighter and thinner than woven fabrics, due to the looser, more open knit structure. |
| Breathability | Woven fabrics can be less breathable than knit fabrics, due to the tight weave. | Knit fabrics are often more breathable than woven fabrics, due to the open knit structure. |
| Shape Retention | Woven fabrics tend to hold their shape better over time, due to the rigid structure. | Knit fabrics can lose their shape more easily over time, due to the stretchy nature of the fabric. |
| Wrinkling | Woven fabrics are more prone to wrinkling and creasing than knit fabrics. | Knit fabrics are generally less prone to wrinkling and creasing than woven fabrics. |
| Tailoring | Woven fabrics are well-suited for tailoring, due to the structured nature of the fabric. | Knit fabrics can be more difficult to tailor due to their stretchy nature. |
| Care | Woven fabrics can be more difficult to care for than knit fabrics, often requiring ironing or dry cleaning. | Knit fabrics are generally easier to care for and can often be machine washed and dried. |
| Price | Woven fabrics are often more expensive than knit fabrics, due to the time and labor involved in the production process. | Knit fabrics are generally less expensive than woven fabrics, due to the less complex production process. |
| Transparency | Woven fabrics are less likely to be see-through than knit fabrics. | Knit fabrics are often more see-through than woven fabrics. |
| Stretch Recovery | Woven fabrics do not have stretch recovery, meaning they do not return to their original shape after stretching. | Knit fabrics have stretch recovery, meaning they can be stretched and then return to their original shape. |
| Shrinkage | Woven fabrics are less prone to shrinking than knit fabrics, due to the tightly woven yarns. | Knit fabrics can be prone to shrinking, especially if they are made from natural fibers such as cotton or wool. |
| Draping | Woven fabrics tend to have a more structured and rigid drape, which can make them less suitable for fluid or flowing designs. | Knit fabrics have a more fluid and flexible drape, making them well-suited for designs that require movement and flow. |
| Comfort | Woven fabrics can be less comfortable than knit fabrics due to their rigid structure and lack of stretch. | Knit fabrics are often more comfortable to wear than woven fabrics due to their flexibility and stretch. |
| Insulation | Woven fabrics can be more insulating than knit fabrics due to their denser structure. | Knit fabrics are often less insulating than woven fabrics due to their open knit structure. |
| Water Resistance | Woven fabrics can be more water-resistant than knit fabrics due to their tightly woven structure. | Knit fabrics are often less water-resistant than woven fabrics due to their more open knit structure. |
| Design Options | Woven fabrics offer a wide range of design options, including different weave patterns, colors, and textures. | Knit fabrics offer a wide range of design options, including different knit patterns, colors, and textures. |
| Versatility | Woven fabrics can be used for a wide range of garments and applications, from formalwear to upholstery. | Knit fabrics are often limited to more casual or athletic wear applications. |
| Environmental Impact | Woven fabrics can have a higher environmental impact due to the more complex production process and higher use of resources. | Knit fabrics can have a lower environmental impact due to the simpler production process and lower use of resources. |
In summary, woven and knit fabrics each have their strengths and weaknesses, and each is better suited for certain types of garments. Woven fabrics are ideal for structured garments that require durability and intricate designs, while knit fabrics are better suited for stretchy and comfortable garments that require ease of movement.